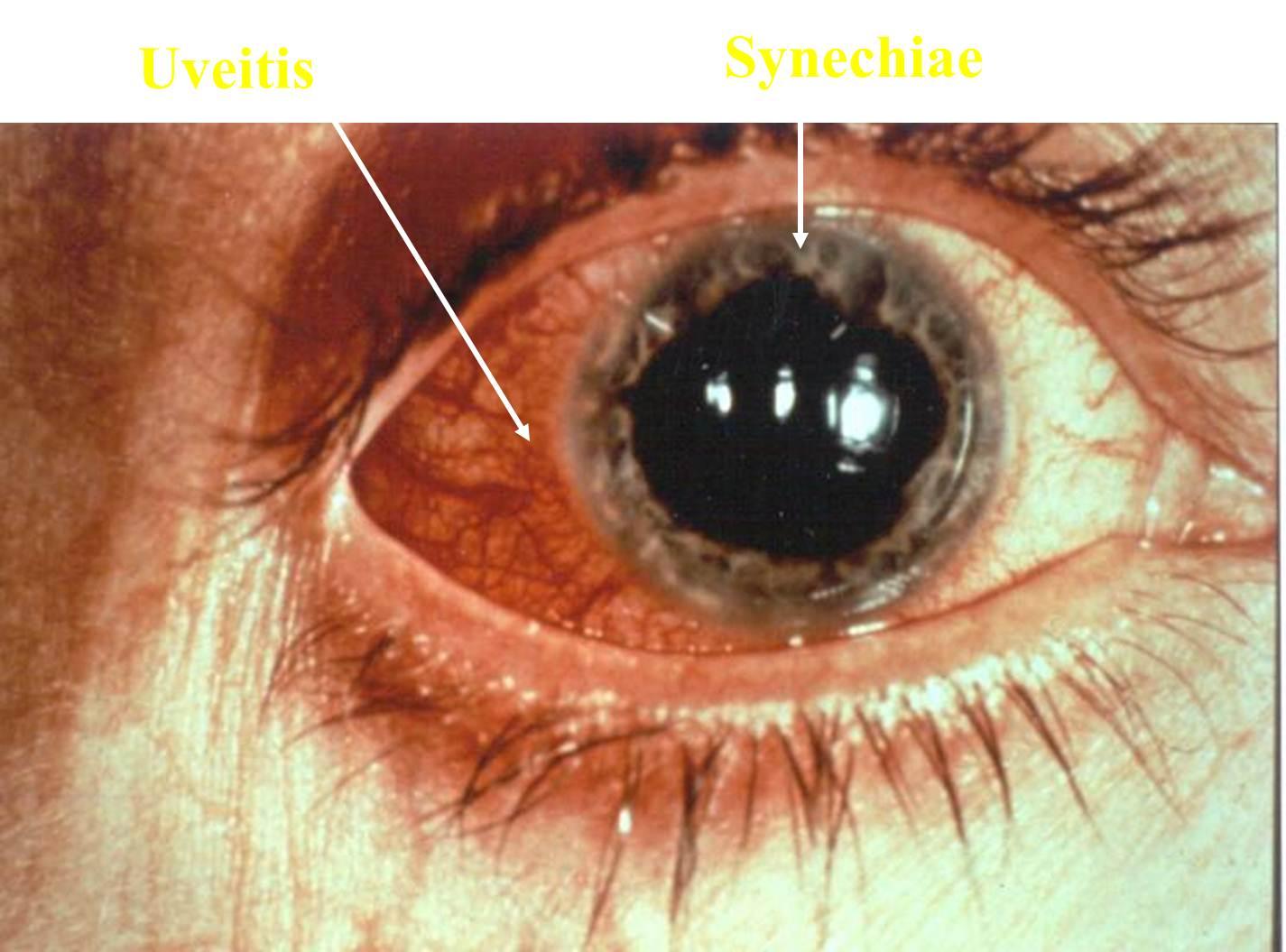
Uveitis is inflammation of the 'uvea' of the eye. The uvea is made up of three parts. The first part is the iris, which is the colored ring of tissue you can see in the mirror. The dark hole in the middle of the iris is the pupil. The second and third parts, which you cannot see directly when looking in a mirror, are the ciliary body and the choroid. They are located behind the iris. An ophthalmologist can visualize them using special examination equipment
Inflammation of the iris is called iritis. Inflammation of the ciliary body is called intermediate uveitis or cyclitis. Inflammation of the choroid is called choroiditis. Inflammation of all three is called panuveitis.
There are several causes of uveitis, including autoimmune disorders (such as sarcoidosis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Behcet's disease, and ankylosing spondylitis), infections (such as syphilis and toxoplasmosis), and trauma. Additionally, some are “idiopathic,” meaning the cause is unknown.
